LISN-Linear impedance stabilization network
Related Terms Explained:
- Definition of: LISN .Linear impedance matching network;
- Definition of: amn, artificial power network ;
- Definition of: an, artificial network ;
- Definition of: ISN, impedance stabilization network.
AMN is one of the classifications of LISN, V-LISN.
AN is a collective term for all networks.
ISN is one of the classifications of LISN, i.e. T-LISN.
The role of LISN linear impedance stabilization networks:
- Provide the necessary supply voltage (AC or DC) and current to the equipment under test (EUT).
- Couple the interference voltage generated by the test equipment and provide it to the test receiver ESR or receiver ESW.
- Provides an explicit RF impedance for the equipment under test (EUT), specifying the impedance as viewed from the EUT's equipment under test end.
- Avoiding noise interference from the power supply (filter)
- Protect the mains supply from stray interference voltages generated by the equipment under test.
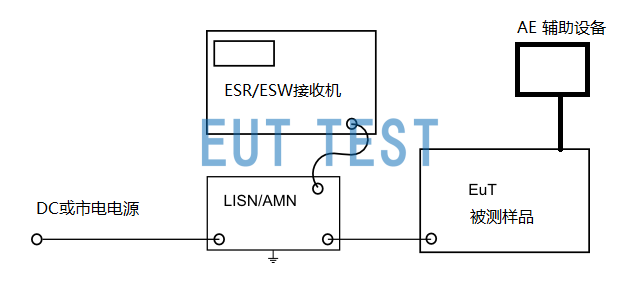
Test Connection Configuration Diagram for LISN and AMN
Design Principles:
The following diagram shows the voltage relationship for a two-wire system with independent grounding. symmetric: symmetrical wire; unsymmetric: unsymmetrical wire
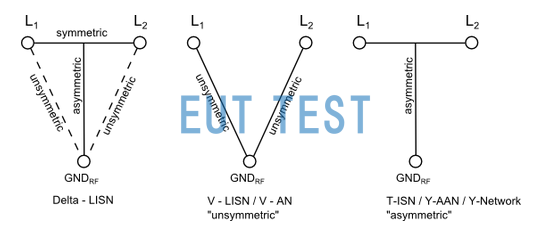
LISN and AMN Symmetric: symmetric line; unsymmetric: asymmetric line
V-Linear Impedance Stabilization Network: V-LISN
V-LISN V-type artificial power networkMeasure the asymmetrical interference voltage between the two lines L1-GND or L2-GND respectively.
V-LISN is also known as V-AMN (artificial power network).V-LISN is the most commonly used LISN today.
V-type artificial power networks are available with two different impedances, which need to be taken into account when selecting the model number. If you have questions about the technical parameters of the SCHWARZBECK-LISN, you can contact EUTTEST for advice.
- ①, In general, V-LISNs with 5μh inductance comply with standards CISPR 16-1-2, CISPR 25, ISO 7637, DO160, and are typically used for measurements on equipment in vehicles, ships, and airplanes that are connected to the onboard power supply via DC or 400Hz.
- ②, another 50 μh V-LISN will operate at 50 Hz or 60 Hz supply frequency. Complying with standards CISPR 16-1-2, MIL Std 461 and ANSI C63.4.
T-Linear Impedance Stabilization Network: T-LISN
T-ISN measures asymmetrical interference voltage (common-mode voltage (electronics)) and provides it to the EMI receiver.T-IS is typically used for measurements on telecommunications and data transmission equipment connected to symmetrical lines such as twisted pairs.
Δ-type linear impedance stabilization network: Δ-LISN
There is a 150 Ω Δ-type artificial power supply network (applicable to the frequency range of 150 kHz ~ 30 MHz), the artificial power supply network between its terminals and the two terminals are connected to the reference ground between the impedance of the mode should be (150 ± 20) Ω, the phase angle shall not exceed 20 °.
When measuring symmetrical voltages, a shielded, balanced transformer is used. In order to avoid significant variations in the impedance network, the input impedance of the transformer should not be lower than 10002 at the frequency of interest.The voltage measured by the measuring receiver depends on the element values and transformation ratios of the network. The network shall be calibrated.
- Created on: 2025-02-25 19:22:27 ;
- Last modified on 2025-02-25 19:40:00 ;
